Introduction

In the realm of modern engineering, the nitinol engine stands out as a fascinating innovation that harnesses the unique properties of shape memory alloys. This technology leverages the remarkable characteristics of nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy, to create engines that can operate with impressive efficiency and versatility. But what is a nitinol engine? Simply put, it’s an engine that utilizes the thermal expansion and contraction properties of nitinol to convert heat energy into mechanical work.
Overview of Nitinol Engine Technology
Nitinol engine technology is revolutionizing how we think about energy conversion and mechanical systems. By exploiting the shape memory effect inherent in nitinol, these engines can perform work efficiently with minimal moving parts. This not only reduces wear and tear but also enhances longevity—two critical factors in any engine's performance.
Importance of Efficiency in Engines
Efficiency is paramount in any engine design; it determines how effectively fuel or energy sources are converted into usable power. In an era where sustainability and reduced carbon footprints are essential, understanding what is the efficiency of a nitinol engine becomes crucial for both manufacturers and consumers alike. An efficient engine not only saves resources but also minimizes environmental impact, making advancements in technologies like the nitinol memory metal heat engine particularly relevant.
What Makes Nitinol Unique
What makes nitinol truly unique lies in its ability to return to its original shape when heated after being deformed at lower temperatures. This characteristic allows for innovative applications across various engineering fields, from automotive to aerospace industries. However, it's essential to consider what are the problems with nitinol as well; challenges such as limitations in temperature resistance and production costs can hinder widespread adoption despite its promising advantages.
Understanding the Nitinol Engine
The nitinol engine represents a fascinating convergence of materials science and mechanical engineering, harnessing the unique properties of shape memory alloys to create innovative energy solutions. By leveraging these properties, the nitinol engine offers a promising alternative to traditional engines, pushing boundaries in efficiency and application. So, what exactly is a nitinol engine?
What is a nitinol engine?
A nitinol engine is an innovative type of heat engine that utilizes nitinol—an alloy primarily composed of nickel and titanium—to convert thermal energy into mechanical work. The unique characteristic of nitinol lies in its ability to return to a predetermined shape when heated, making it an ideal candidate for applications requiring efficient movement and energy conversion. In essence, the nitinol engine operates on principles that differ significantly from conventional engines, offering intriguing possibilities for future technologies.
When we ask ourselves, What is the efficiency of a nitinol engine? it's important to note that these engines can potentially achieve higher efficiencies than their traditional counterparts by minimizing waste heat and optimizing thermal cycles. This efficiency stems from the remarkable properties of shape memory alloys that allow for continuous operation with minimal energy loss. As research progresses, we may soon witness even more refined designs that push efficiency levels further.
The Science Behind Nitinol Shape Memory Alloys
The science behind Nitinol shape memory alloys is both intricate and fascinating, rooted in phase transformation phenomena within metallic structures. When subjected to specific temperature ranges, Nitinol can transition between two distinct crystalline forms: martensite at lower temperatures and austenite at higher temperatures. This reversible transformation allows the alloy not only to remember its original shape but also to generate significant force during heating or cooling processes.
Understanding how this phase change contributes to the function of a nitinol engine reveals why it's garnering attention in various fields—especially where compactness and lightweight design are critical factors. As researchers continue exploring ways to enhance these properties further, we might find ourselves asking: What are the problems with nitinol? While there are challenges associated with durability and cost-effectiveness in production processes, ongoing advancements aim to mitigate these issues.
Applications of Nitinol in Engineering
Nitinol's versatility extends across numerous engineering applications—from medical devices like stents and guidewires to robotics where precise movements are essential. In particular, its use in creating actuators for robotic systems showcases how well-suited this material is for tasks requiring reliable motion without bulky components or complex mechanisms. Furthermore, as interest grows around sustainable technologies, applications involving nitinol engines could revolutionize energy systems across various industries.
The potential impact on sectors such as automotive or aerospace cannot be overstated; imagine lightweight vehicles powered by highly efficient nitinol engines that drastically reduce fuel consumption! Additionally, ongoing research into what is considered “the most efficient heat engine possible” often includes discussions surrounding innovations using shape memory alloys like Nitinol due to their inherent advantages over conventional materials.
As we continue our exploration into this remarkable technology's capabilities and limitations—including considerations around cost implications—it becomes clear that understanding both its benefits and challenges will be key moving forward. With each advancement made in refining the design of the Nitinol Memory Metal Heat Engine comes renewed hope for greater efficiencies that could reshape our approach toward energy conversion.
Analyzing Efficiency Factors

When it comes to engines, efficiency is the name of the game, and the nitinol engine is no exception. Understanding how efficient a nitinol engine can be is crucial for its potential applications across various industries. By examining its efficiency metrics, we can better appreciate what sets this revolutionary technology apart from traditional engines.
What is the efficiency of a nitinol engine?
The efficiency of a nitinol engine hinges on its unique properties as a shape memory alloy. Generally speaking, these engines can achieve efficiencies around 30-40%, depending on design and operational conditions. This level of performance places the nitinol engine in direct competition with other heat engines, making it an attractive option for energy conversion applications.
What is particularly fascinating about the efficiency of a nitinol engine is how it utilizes thermal energy to induce movement based on temperature changes. The transformation between phases—martensite and austenite—enables these engines to convert heat into mechanical work effectively. However, there are limits to this efficiency that need careful consideration, especially regarding operational temperatures and material fatigue.
Comparing Nitinol with Other Engine Types
In comparing the nitinol engine with other types such as internal combustion or steam engines, distinct advantages emerge alongside notable drawbacks. While traditional engines often rely heavily on fossil fuels and have lower thermal efficiencies due to waste heat loss, the nitinol engine leverages thermal cycles more effectively. This makes it not only more environmentally friendly but also potentially less costly in terms of fuel consumption.
However, what are the problems with nitinol when stacked against conventional options? One major hurdle lies in material costs and production challenges that make scaling up difficult compared to established technologies like gas turbines or diesel engines. Additionally, while its lightweight design offers benefits in many applications, it may falter under extreme conditions where other materials might perform better.
Role of Heat Exchange in Efficiency
Heat exchange plays a pivotal role in determining how efficiently a nitinol engine operates as it directly impacts energy conversion rates. The effectiveness of heat exchangers can significantly enhance or diminish overall performance by optimizing how thermal energy is transferred within the system. Efficient heat exchange mechanisms allow for quicker phase transformations in the nitinol material itself, thereby maximizing output from minimal input.
Moreover, understanding what is the most efficient heat engine possible leads us back to innovations like those seen in advanced designs utilizing nitinol technology. Engineers are continuously exploring ways to improve heat transfer rates within these systems while minimizing losses through radiation or convection. Ultimately, effective heat management could be key not just for improving existing designs but also for unlocking new applications for Nitinol Memory Metal Heat Engines across diverse sectors.
Benefits of Nitinol Engines
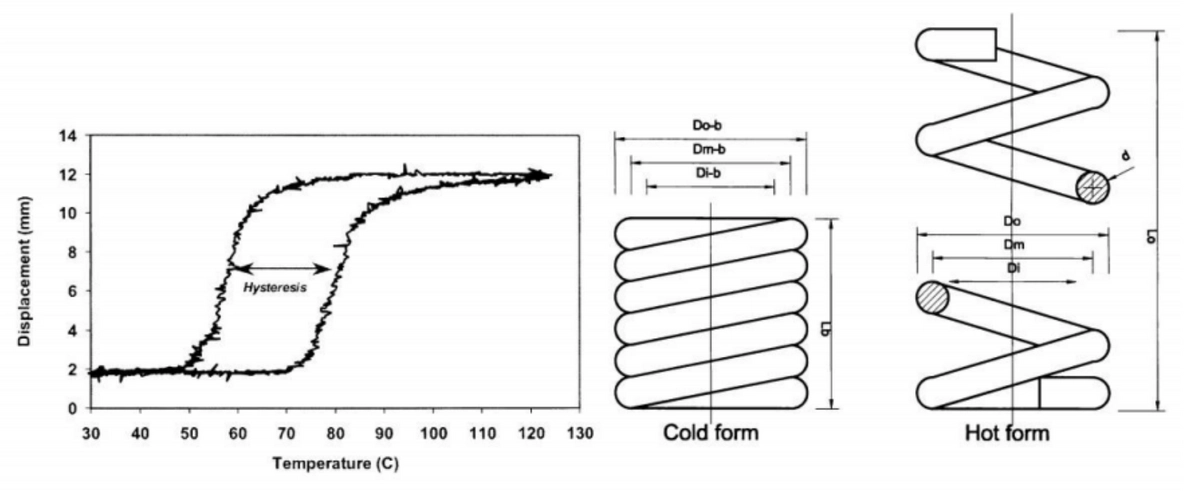
Nitinol engines are gaining recognition for their unique advantages that set them apart from traditional engine technologies. These engines leverage the remarkable properties of nitinol, a shape memory alloy, to enhance energy conversion processes and overall efficiency. As industries increasingly seek sustainable and efficient solutions, the benefits of nitinol engines are becoming more relevant than ever.
Advantages in Energy Conversion
One of the standout features of a nitinol engine is its ability to convert thermal energy into mechanical work with impressive efficiency. What is the efficiency of a nitinol engine? Research indicates that these engines can achieve higher efficiencies compared to conventional combustion engines due to their innovative design and material properties. The unique shape memory effect allows for better thermal cycling and energy capture, leading to superior performance in various applications.
Moreover, the energy conversion process in a nitinol engine minimizes waste heat generation, making it an environmentally friendly option. By optimizing how heat is utilized within the system, these engines can significantly reduce fuel consumption while maintaining high output levels. This advantage positions nitinol technology as a key player in advancing sustainable engineering practices.
Lightweight Design and Its Impact
The lightweight nature of nitinol components plays a crucial role in enhancing overall engine performance and efficiency. A typical question arises: What is a nitinol engine? It’s an innovative device that uses this lightweight material to produce motion through thermal activation rather than relying solely on heavy metals or complex mechanisms common in traditional engines. This reduction in weight not only improves fuel economy but also leads to increased maneuverability across various applications.
Additionally, lighter designs contribute to reduced manufacturing costs and simpler assembly processes, which can make production more efficient overall. The impact on transportation industries is particularly noteworthy; vehicles equipped with nitinol-based systems can achieve greater speeds while consuming less energy due to their reduced mass. In essence, the lightweight design inherent in nitinol engines revolutionizes how we think about power-to-weight ratios.
Versatility Across Different Industries
Nitinol technology shines brightly when it comes to versatility across diverse industries—from aerospace and automotive to medical devices and robotics. The adaptability of a nitinol engine allows it to be tailored for specific applications without compromising performance or efficiency levels; this flexibility makes it an attractive option for engineers looking for innovative solutions. For instance, what are the problems with nitinol? While challenges exist regarding temperature resistance and cost implications, ongoing research continues to unlock new possibilities for integration into various sectors.
In aerospace applications, where weight savings translate directly into fuel savings, using a Nitinol Memory Metal Heat Engine could lead to groundbreaking advancements in flight technology. In medical devices, its biocompatibility combined with its unique mechanical properties opens doors for novel therapeutic tools that respond dynamically within the human body—showing just how versatile this alloy truly is! With such broad applicability across different fields, it's clear that nitinol technology holds immense potential for future innovations.
Challenges Concerning Nitinol

While the nitinol engine presents exciting possibilities, it is not without its challenges. Understanding these problems is crucial for future development and optimization of this innovative technology. From material limitations to production costs, several factors hinder the widespread adoption of nitinol engines.
What are the problems with nitinol?
One of the primary issues with nitinol is its complex behavior under varying conditions. The unique properties that make a nitinol engine efficient—such as shape memory and superelasticity—can also lead to unpredictable performance in extreme environments. Additionally, there are concerns about fatigue over time, which could impact the longevity and reliability of a nitinol engine.
Another significant problem lies in its manufacturing process, which can be intricate and labor-intensive. This complexity may lead to inconsistencies in quality and performance across different batches of nitinol components. Furthermore, while researchers explore applications for a nitinol memory metal heat engine, scalability remains a challenge that needs addressing for practical implementation.
Limitations in Temperature Resistance
Temperature resistance is another critical limitation for the nitinol engine's potential applications. Although these alloys can operate efficiently within certain temperature ranges, they struggle at higher temperatures compared to traditional materials used in engines today. For instance, while some engines thrive on high-temperature combustion processes, a conventional nitinol engine may not withstand such extremes without losing structural integrity.
This limitation raises questions about what is the efficiency of a nitinol engine when subjected to fluctuating thermal conditions typical in many industrial applications. Engineers must carefully design systems around these constraints to ensure optimal performance without compromising safety or durability. As research continues into improving temperature resistance, we might see breakthroughs that enhance the viability of this promising technology.
Cost Implications in Production
The cost implications associated with producing components for a nitinol engine cannot be overlooked either. While advancements have been made in manufacturing methods, producing high-quality shape memory alloys still requires significant investment and specialized techniques that drive up costs compared to more established materials like steel or aluminum. This price disparity makes it challenging for manufacturers and engineers to justify switching from conventional engines to those utilizing advanced materials like Nitinol.
Moreover, as companies explore what is the most efficient heat engine possible using these alloys, they must balance performance improvements against financial feasibility. If production costs remain high without corresponding efficiency gains or market demand increases significantly, widespread adoption may lag behind expectations set by early research findings on Nitinol Memory Metal Heat Engines.
In conclusion, while there are notable challenges concerning the use of Nitinol technology in engines—including unpredictable performance characteristics under various conditions and cost implications—ongoing research aims to address these hurdles effectively as we look toward future innovations.
Future of Nitinol Technology

The future of nitinol technology is bright and filled with potential, especially as engineers and scientists push the boundaries of what is possible with this remarkable material. The nitinol engine, known for its unique shape memory properties, is poised to revolutionize energy conversion in various applications. But what does the most efficient heat engine possible look like, and how can we get there?
What is the most efficient heat engine possible?
When discussing efficiency in engines, one might wonder: what is the most efficient heat engine possible? Theoretically, it would be an engine that operates at maximum Carnot efficiency, which depends on the temperature difference between the heat source and sink. In practical terms for a nitinol engine, advancements in materials science could lead to engines that utilize nitinol’s shape memory effect more effectively, thereby enhancing overall efficiency.
As researchers delve deeper into optimizing nitinol alloys for higher performance under varying temperatures, we may witness breakthroughs that make these engines not only competitive but possibly superior to traditional forms of energy conversion. Imagine a world where a nitinol memory metal heat engine could convert waste heat into usable energy with unprecedented effectiveness! This vision isn't just a pipe dream; it's becoming increasingly attainable through ongoing research.
Innovations on the Horizon
Innovations are indeed on the horizon for nitinol technology! Researchers are exploring new alloy compositions and treatments that could enhance the thermal properties of nitinol engines while addressing existing challenges such as temperature resistance. These innovations may lead to more robust designs capable of operating in extreme conditions without compromising performance or longevity.
Moreover, integration with smart technologies promises to optimize how these engines operate by dynamically adjusting based on real-time environmental conditions. This adaptability could significantly improve what is the efficiency of a nitinol engine across various applications—from automotive engineering to aerospace technologies—making it an exciting area for future development.
GEE SMA and Advancements in Nitinol
One particularly promising avenue within this field is GEE SMA (Geometric Effect Engine Shape Memory Alloy), which represents cutting-edge advancements in nitinol technology. By harnessing geometric configurations alongside traditional shape memory effects, researchers hope to create even more efficient designs that maximize power output while minimizing material stress and wear over time.
GEE SMA could potentially address some common problems associated with traditional nitinol applications—like limited temperature ranges—by offering enhanced thermal stability and operational flexibility. As these advancements unfold, they will likely redefine our understanding of what constitutes an effective energy conversion mechanism within a nitinol engine framework.
The journey towards maximizing the potential of a nitinol memory metal heat engine continues to be thrilling as innovation drives us closer to achieving unprecedented levels of efficiency!
Conclusion

In summary, the nitinol engine presents a fascinating intersection of material science and engineering innovation. By leveraging the unique properties of nitinol, particularly its shape memory effect, these engines offer intriguing possibilities for efficient energy conversion. However, understanding what is a nitinol engine also means recognizing its limitations and challenges in practical applications.
Key Takeaways on Nitinol Engine Efficiency
What is the efficiency of a nitinol engine? While still under research and development, early studies suggest that these engines can achieve notable efficiency levels compared to traditional engines. Factors such as temperature fluctuations and heat exchange play critical roles in maximizing this efficiency, emphasizing the importance of optimizing design for practical use.
Future Prospects for Nitinol Technology
Looking ahead, advancements in nitinol technology could revolutionize how we approach heat engines. What is the most efficient heat engine possible? With ongoing innovations and research into enhanced materials and designs, future iterations of the nitinol engine may push boundaries further than previously imagined. The potential for applications across various industries—from automotive to aerospace—could redefine standards in energy efficiency.
Final Thoughts on Nitinol Memory Metal Heat Engine
Despite some hurdles—what are the problems with nitinol?—the prospects for the nitinol memory metal heat engine remain bright. Its lightweight design coupled with versatility makes it an appealing choice for modern engineering challenges. As we continue to explore this promising technology, it’s clear that the journey toward optimizing nitinol engines has only just begun.

